

They travel along the surface of the earth and thus cause the most damage. They move up and down or side to side, perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is moving. "S waves" or "secondary waves" are the next waves to be detected.This is certainly what happens as a primary (P) seismic waves pass from the mantle to the (denser) core. So, a decrease in wave velocity usually indicates a rise in density.
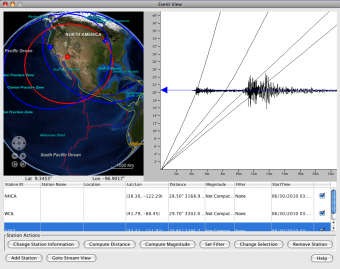
Geologists have studied seismic waves, or shock waves, that are created by earthquake activity. The speed of a seismic wave is proportional to the square root of the modulus (stiffness) of the medium divided by the square root of its density. These are compressional waves that push and pull as they move through rock and fluids. How far down into the Earth does the outer core begin. "P waves" or "primary waves" are the first waves to be detected.When an earthquake occurs, different types of energy waves are generated. In the upper part of the mantle, the earthquake waves slow down. The Moho shows up in seismic data as a distinct change in wave speed due to a. How do rock particles move during the passage of a Primary wave (P-waves) through the. Two other regions regularly exhibiting earthquakes include the Alpide belt, extending along the southern margin of Eurasia through the Himalayan Mountains, Sumatra, and Java and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge running along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean. Molten regions cause P waves to slow down and completely stop S waves. While tectonic earthquakes can occur at any location around the world, the majority of large earthquakes-about 80 percent-occur at the circum-Pacific seismic belt found along the rim of the Pacific Ocean.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
